The Biometric Consortium's charter was formally approved
on December 7, 1995, by the Facilities Protection Committee,
a committee that reports to the Security Policy Board
through the Security Policy Forum. The Security Policy Board
was established by Presidential Decision Directive/NSC-29 on
September 16, 1994, for the coordination, formulation,
evaluation, and oversight of US national security policy.
The Security Policy Board reports to the Assistant to the
President for National Security Affairs.
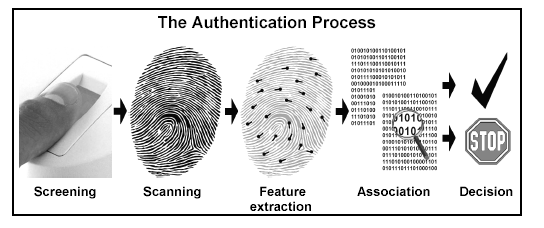
"Biometrics are automated methods of recognizing a person
based on a physiological or behavioral characteristic."
Examples of human traits used for biometric recognition
include fingerprints, speech, face, retina, iris,
handwritten signature, hand geometry, and wrist veins.
Biometric recognition can be used in identification
mode, where the biometric system identifies a person
from the entire enrolled population by searching a database
for a match.
A system also can be used in verification mode,
where the biometric system authenticates a person's claimed
identity from his/her previously enrolled pattern.
Using biometrics for identifying and authenticating human
beings offers some unique advantages. Only biometric
authentication bases an identification on an intrinsic part
of a human being. Tokens, such as smart cards, magnetic
stripe cards, physical keys, and so forth, can be lost,
stolen, duplicated, or left at home. Passwords can be
forgotten, shared, or observed.
While all biometric systems have their own advantages and
disadvantages, there are some common characteristics needed
to make a biometric system usable.
First, the biometric must be based upon a distinguishable
trait. For example, for nearly a century, law enforcement
has used fingerprints to identify people. There is
a great deal of scientific data supporting the idea that "no
two fingerprints are alike."
Newer methods, even those with a great deal of scientific
support, such as DNA-based genetic matching, sometimes do
not hold up in court.
Another key aspect is how user-friendly is the
system? Most people find it acceptable to have their
pictures taken by video cameras or to speak into a
microphone. In the United States, using a fingerprint sensor
does not seem to be much of a problem. In some other
countries, however, there is strong cultural opposition to
touching something that has been touched by many other
people.
While cost is always a concern, most implementers today
are sophisticated enough to understand that it is not only
the initial cost of the sensor or the matching software that
is involved. Often, the life-cycle support cost of providing
system administration support and an enrollment operator can
overtake the initial cost of the hardware. Also of key
importance is accuracy. Some terms that are used to describe
the accuracy of biometric systems include
false-acceptance rate (percentage of impostors
accepted), false-rejection rate (percentage of
authorized users rejected), and equal-error rate
(when the decision threshold is adjusted so that the false-
acceptance rate equals the false-rejection rate).
When discussing the accuracy of a biometric system, it is
often beneficial to talk about the equal-error rate or at
least to consider the false-acceptance rate and
false-rejection rate together. For many systems, the
threshold can be adjusted to ensure that virtually no
impostors will be accepted. Unfortunately, this often means
an unreasonably high number of authorized users will be
rejected.
To summarize, a good biometric system is one that is low
cost, fast, accurate, and easy to use."
We at Biometrics Direct believe our solutions are among
the best in the industry. A special emphasis of our
company’s vision is the utilization of advanced biometric
technology to increase the security of our clients’ homes,
workplaces, networks and data. The small and medium
business environments make up the bulk of the US economy and
their security is fundamental to the defense of our national
financial system. Effective solutions must offer increased
security of data, networks and access to facilities while
maintaining personal privacy.

